集群健康状态相关
查看集群健康状态
1 | GET _cluster/health |
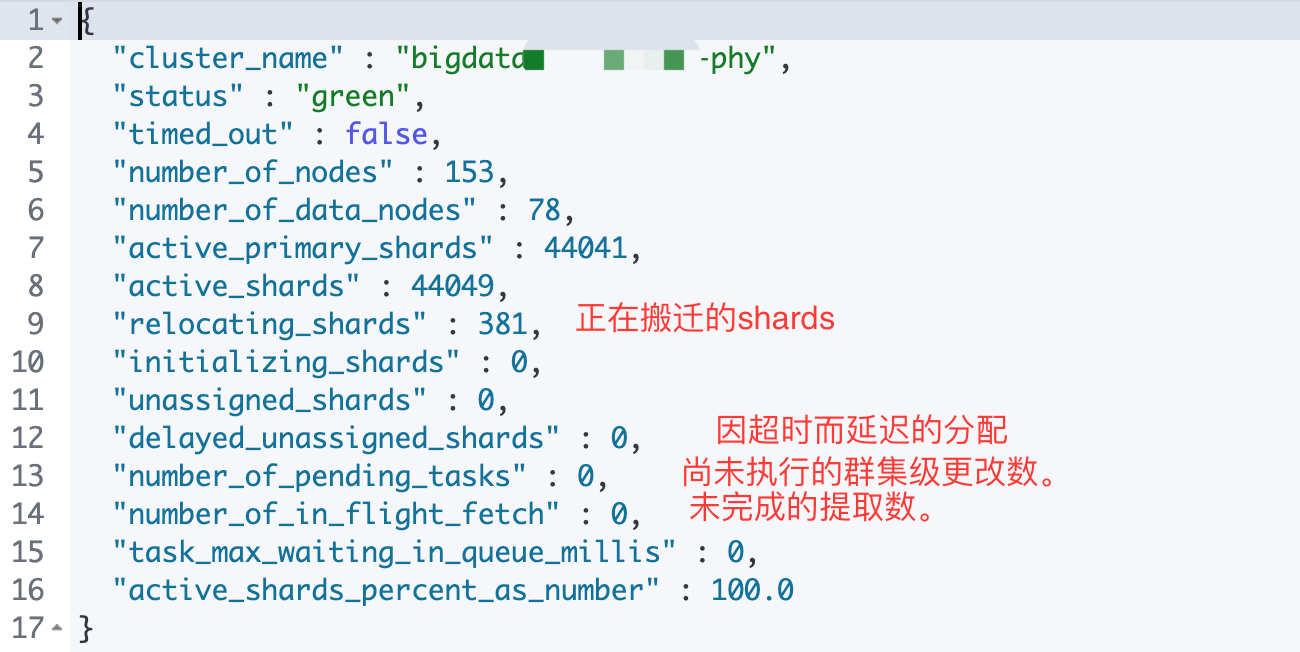 number_of_pending_tasks:是指主节点创建索引并分配shards等任务,如果该指标数值一直未减小代表集群存在不稳定因素 。
number_of_pending_tasks:是指主节点创建索引并分配shards等任务,如果该指标数值一直未减小代表集群存在不稳定因素 。
查看未分配原因
1 | GET _cluster/allocation/explain |
有以下几种可能
- INDEX_CREATED : Unassigned as a result of an API creation of an index. 索引创建 : 由于API创建索引而未分配的
- CLUSTER_RECOVERED : Unassigned as a result of a full cluster recovery. 集群恢复 : 由于整个集群恢复而未分配
- INDEX_REOPENED : Unassigned as a result of opening a closed index. 索引重新打开
- DANGLING_INDEX_IMPORTED : Unassigned as a result of importing a dangling index. 导入危险的索引
- NEW_INDEX_RESTORED : Unassigned as a result of restoring into a new index. 重新恢复一个新索引
- EXISTING_INDEX_RESTORED : Unassigned as a result of restoring into a closed index. 重新恢复一个已关闭的索引
- REPLICA_ADDED : Unassigned as a result of explicit addition of a replica. 添加副本
- ALLOCATION_FAILED : Unassigned as a result of a failed allocation of the shard. 分配分片失败
- NODE_LEFT : Unassigned as a result of the node hosting it leaving the cluster. 集群中节点丢失
- REROUTE_CANCELLED : Unassigned as a result of explicit cancel reroute command. reroute命令取消
- REINITIALIZED : When a shard moves from started back to initializing, for example, with shadow replicas. 重新初始化
- REALLOCATED_REPLICA : A better replica location is identified and causes the existing replica allocation to be cancelled. 重新分配副本
查看具体索引未分配或不搬迁的原因
1 | GET _cluster/allocation/explain |
返回结果: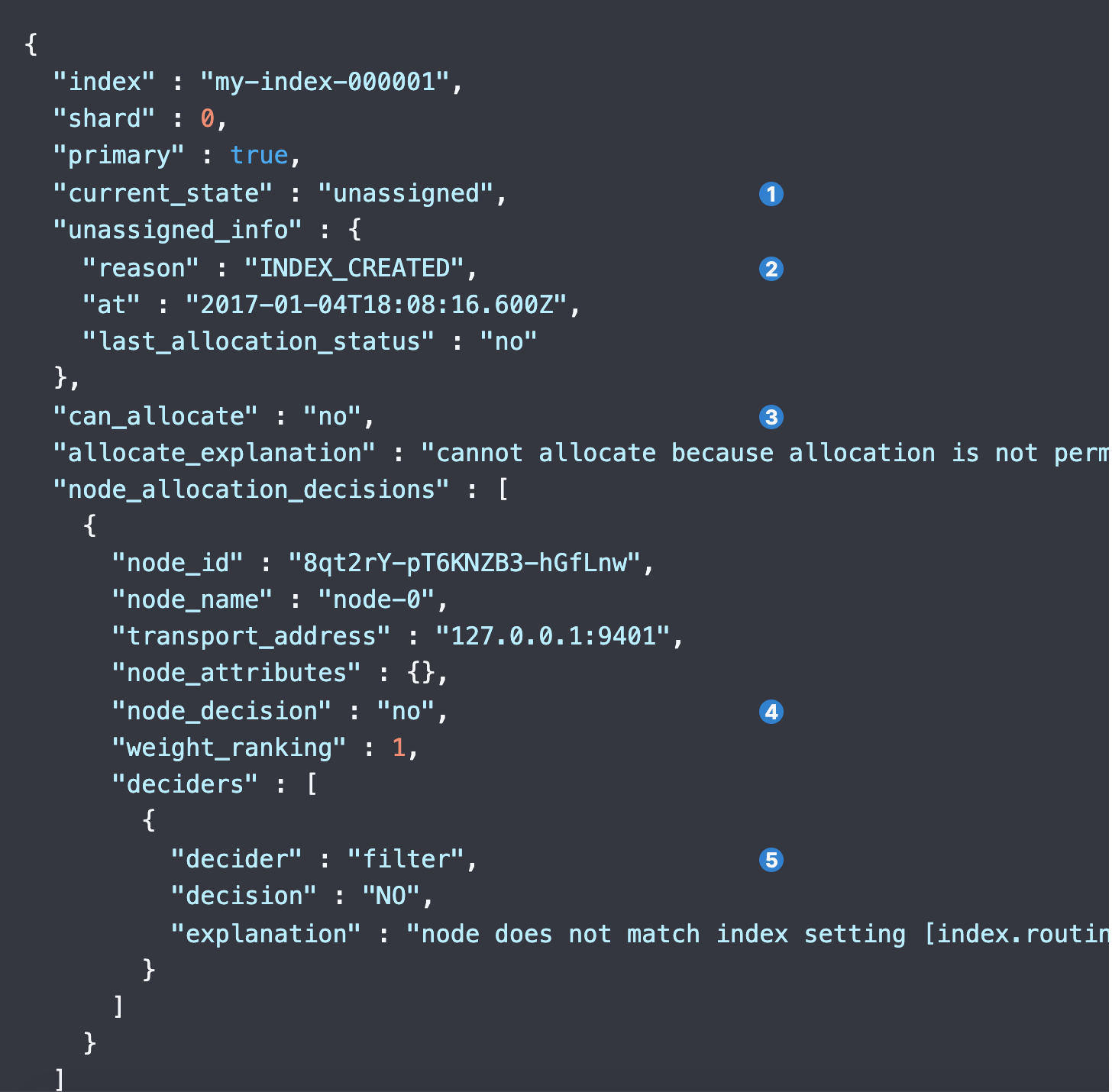
- The current state of the shard.
- The reason for the shard originally becoming unassigned.
- Whether to allocate the shard.
- Whether to allocate the shard to the particular node.
- The decider which led to the no decision for the node.导致该节点没有决策的决策器。
- An explanation as to why the decider returned a no decision, with a helpful hint pointing to the setting that led to the decision. 解释为什么决策器返回“否”决策,并提供一个有用的提示,指出导致该决策的设置。
解释一个索引为什么分配到该节点
1 | GET _cluster/allocation/explain |
重新尝试分配失败的shard
1 | POST _cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true |
查看等待中的任务
1 | GET _cat/pending_tasks |
可以看到任务都被指派了优先级( 比如说 URGENT 要比 HIGH 更早的处理 )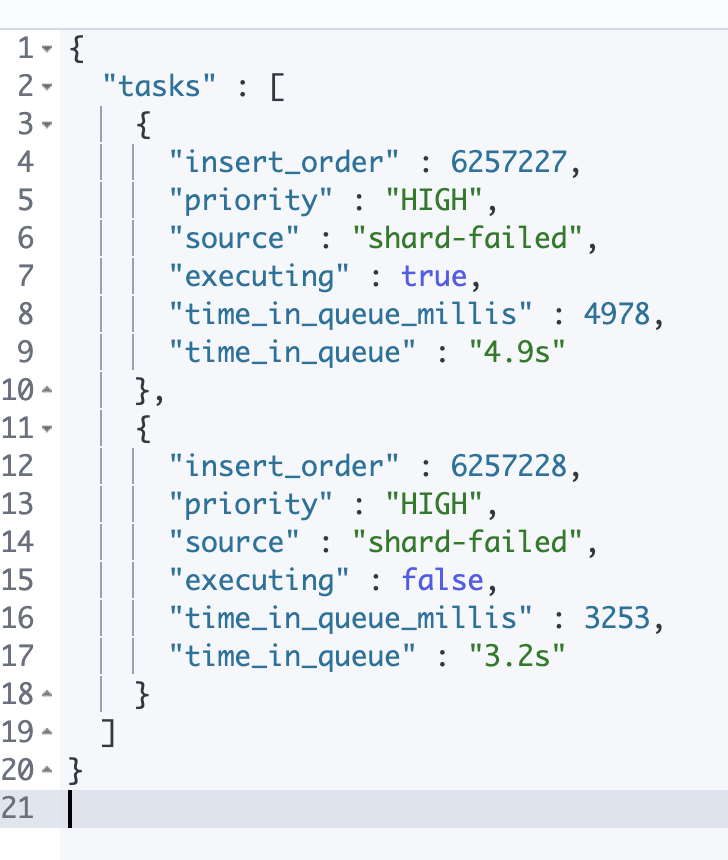
查看nodes
1 | GET _cat/nodes |
查看active master
1 | GET _cat/master |
查看集群内正在搬迁的索引
1 | GET _cat/recovery?v&h=index,shard,time,type,stage,source_node,target_node,files_percent,bytes_percent,translog_ops_percent&s=type:desc,stage,shard&active_only |
索引相关
查看index配置信息
1 | GET index_name/_settings?flat_settings |
查看默认配置
1 | GET index_name/_settings?flat_settings&include_defaults |
查看index的mapping信息
1 | GET index_name/_mapping |
查看index的模板
1 | GET _template/us01_rlib_dbroker.d-engine.sailing |
查看index的shard信息
1 | GET _cat/shards/index_name |
修改索引默认延时
默认情况,集群会等待一分钟来查看节点是否会重新加入,如果这个节点在此期间重新加入,重新加入的节点会保持其现有的分片数据,不会触发新的分片分配。
通过修改参数 delayed_timeout ,默认等待时间可以全局设置也可以在索引级别进行修改:
1 | PUT /_all/_settings |
通过使用 _all 索引名,我们可以为集群里面的所有的索引使用这个参数。默认时间被修改成了 5 分钟。
这个配置是动态的,可以在运行时进行修改。如果你希望分片立即分配而不想等待,你可以设置参数: delayed_timeout: 0.
延迟分配不会阻止副本被提拔为主分片。集群还是会进行必要的提拔来让集群回到 yellow 状态。缺失副本的重建是唯一被延迟的过程。
索引搬迁
1 | POST _cluster/reroute |
取消索引搬迁
1 |
|
索引shard重定向(丢弃shard)
1 | POST /_cluster/reroute |
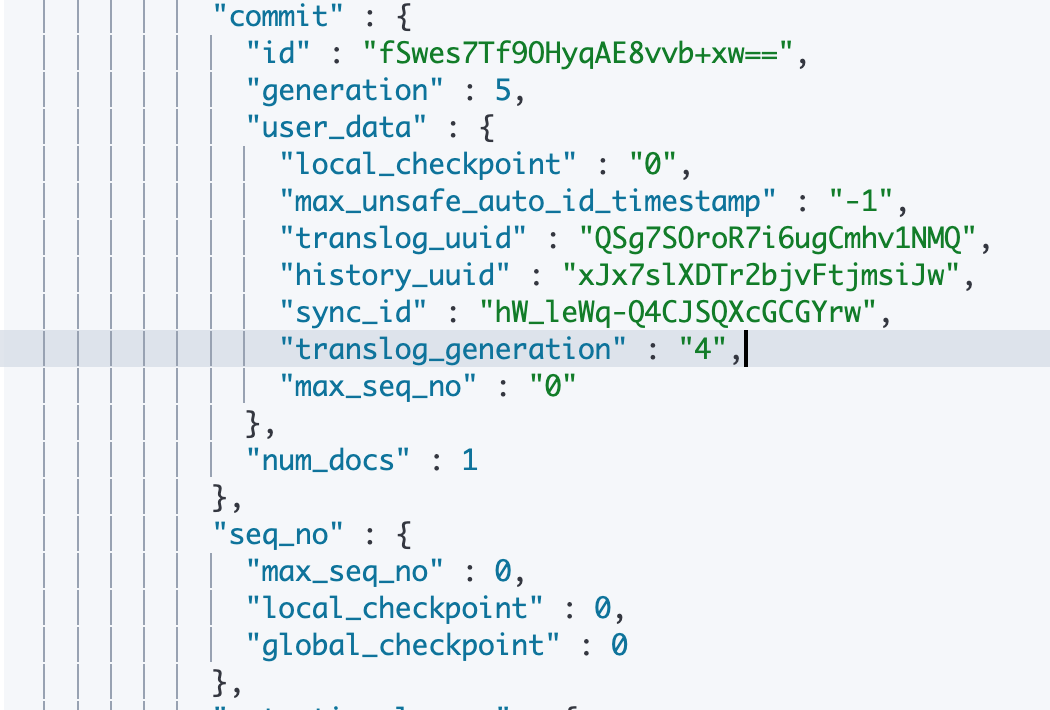
查看索引checkpoint信息
1 | GET /index_name/_stats?level=shards //index_name表示对应的索引 |
索引reindex
1 | POST _reindex |
迁移shard到别的节点
1 | POST _cluster/reroute |
集群相关的设置
查看节点配置的线程池大小
1 | GET _cat/thread_pool/write?v&h=node_name,size |
临时关闭磁盘检测加快master处理速度
1 | PUT _cluster/settings?master_timeout=360s |
集群级别排除某台机器
1 | PUT _cluster/settings?flat_settings |
也可索引级别排除某台机器
1 | PUT router_access_20210401/_settings |
日志级别设置
所有日志(全局不建议开启,容易导致线上故障)
1 | PUT _cluster/settings |
单个类或者模块
1 | PUT _cluster/settings |
集群的迁移参数
- cluster.routing.allocation.enable
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| all | 允许所有类型shard进行shard分配 |
| primaries | 允许主分片进行shard分配 |
| new_primaries | 允许新索引的主分片分配 |
| none | 所有类型的分片都不可分配 |
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_incoming_recoveries , 一个节点上允许发生多少个并发的传入分片恢复。传入恢复是指在节点上分配目标分片(很可能是复制副本,除非分片正在重新定位)。默认为2
cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_outgoing_recoveries(同上,传出)
cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries(最大初始化主分片的个数),虽然副本的恢复通过网络进行,但节点重新启动后未分配的主节点的恢复将使用本地磁盘中的数据。这些恢复应该很快,以便在同一个节点上并行进行更多的初始主恢复。默认为4。
cluster.routing.allocation.same_shard.host ,允许根据主机名和主机地址执行检查以防止在单个主机上分配同一个碎片的多个实例。默认值为false,表示默认情况下不执行任何检查。此设置仅适用于在同一台计算机上启动多个节点的情况。
shard均衡的设置
cluster.routing.rebalance.enable
参数 含义 all 允许对所有分片进行均衡 primaries 只对主分片进行均衡 replicas 只对副本分片进行均衡 none 对所有分片都不进行均衡 cluster.routing.allocation.allow_rebalance
参数 含义 always 始终允许重新均衡 indices_primaries_active 只有当群集中的所有主分片都被分配时。 indices_all_active 只有当群集中的所有分片都被分配时。(默认) cluster.routing.allocation.cluster_concurrent_rebalance(控制均衡,不控制迁移)
允许控制集群范围内允许多少并发分片重新平衡。默认为2。请注意,此设置仅控制由于集群中的不平衡而同时重新定位分片的数量。此设置不限制由于分配筛选或强制感知而导致的分片重新定位。
基于磁盘的分片分配设置
不能在这些设置中混合使用百分比值和字节值。要么所有值都设置为百分比值,要么全部设置为字节值。这种强制执行使得Elasticsearch可以验证设置是否内部一致,确保低磁盘阈值小于高磁盘阈值,高磁盘阈值小于泛洪水位阈值。
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.threshold_enabled(是否打开磁盘分配决策器)
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.low(低水位线) 副本分片不在分配的界限,控制磁盘使用的低水位线。默认值为85%,这意味着Elasticsearch不会将碎片分配给磁盘使用率超过85%的节点。也可以将其设置为绝对字节值(如500mb),以防止Elasticsearch在可用空间不足时分配分片。此设置不会影响新创建索引的主分片,但会阻止分配其副本。
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.high(高水位线)重新定位的界限,控制高水位线。默认为90%,这意味着弹性搜索将尝试将分片从磁盘使用率超过90%的节点重新定位。如果分片的可用空间小于指定的数量,也可以将其设置为绝对字节值(类似于低水印),以便将碎片重新定位到远离节点的位置。此设置影响所有碎片的分配,无论以前是否分配。
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.flood_stage(洪水水位线),控制洪水水位线,默认为95%。Elasticsearch强制执行只读索引块(index.blocks.read_only_allow_delete)在节点上分配了一个或多个分片,并且至少有一个磁盘超过泛洪水位的每个索引。此设置是防止节点耗尽磁盘空间的最后手段。当磁盘利用率低于最高值时,索引块将自动释放
cluster.info.update.interval(检查磁盘使用率间隔,默认30s)
cluster.routing.allocation.disk.include_relocations ,默认值为true,这意味着Elasticsearch将在计算节点的磁盘使用量时考虑当前正在重新定位到目标节点的碎片。但是,考虑到重定位碎片的大小可能意味着节点的磁盘使用量估计错误,因为重新定位可能完成90%,最近检索到的磁盘使用量将包括重新定位碎片的总大小以及正在运行的重定位已使用的空间。
index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node. 一个索引在各node最多分配数。可以帮助索引分布均衡。